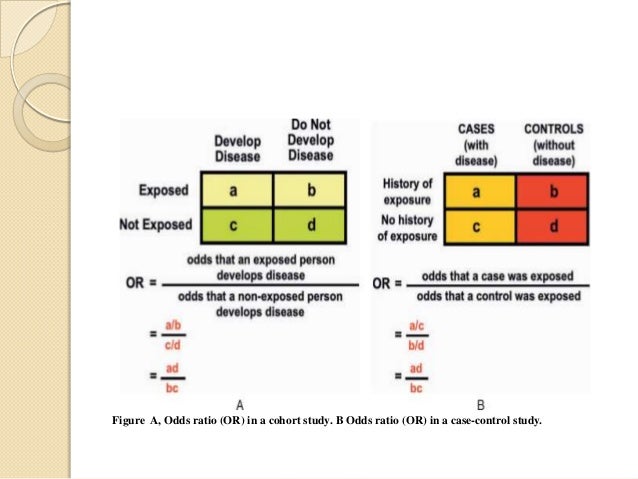
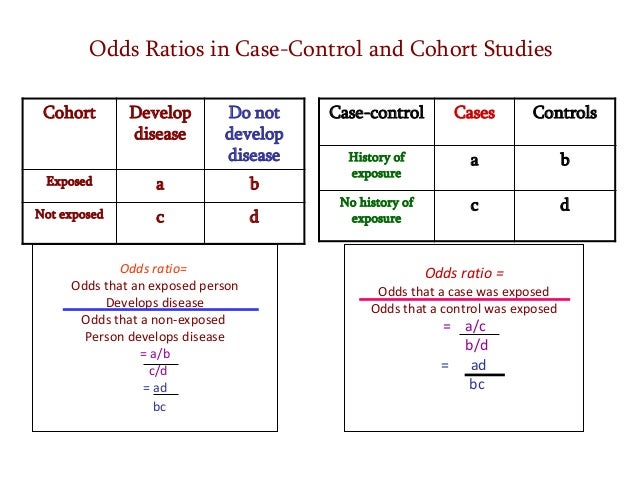
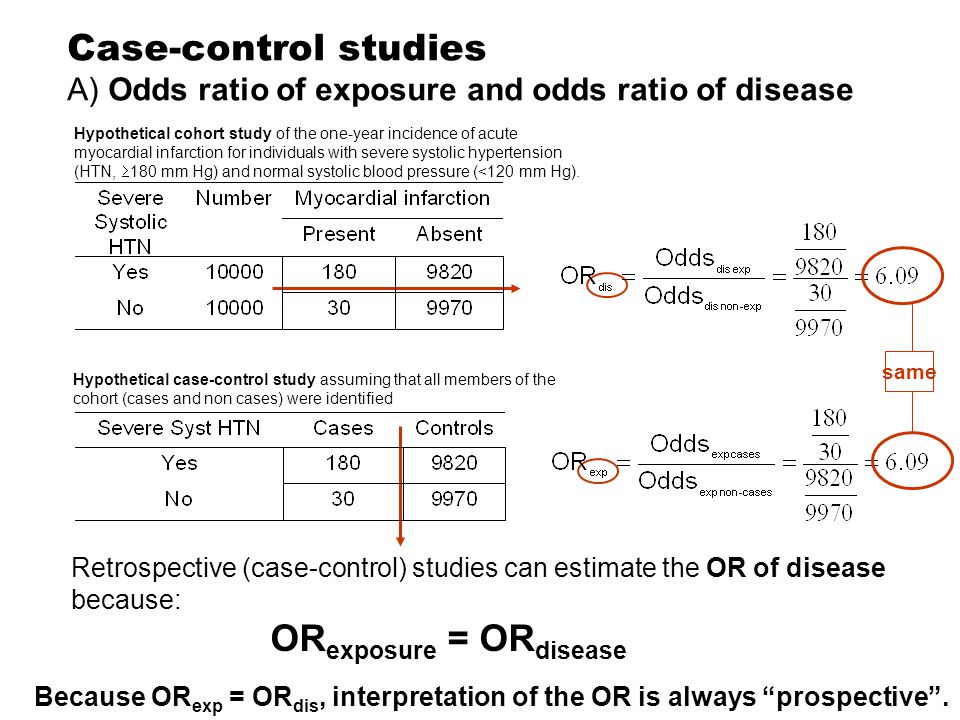
Calculating Odds Ratios Calculating Odds Ratios A study looking at breast cancer in women compared cases with non The odds of exposure in case group a/c = 75/25 = 3 control group b/d = 25/75 = 1/3 both relative risk and the odds ratio are only sensical in wellOct 01, 07 · To understand why the risk ratio is not appropriate in the Knoll's study, we consider the example reported in Figure 1, showing that, unlike the OR, the risk ratio among others depends on the number of controls taken for each caseAs shown in Figure 1 (left panel), the risk ratio for arteriovenous fistula thrombosis results to be 65% higher (risk ratio=165) in patients withWhen we use certain statistical methods (like logistic regression) that output results directly in the form of odds ratios If the risks were 08 and 09, the odds ratio and relative risk will be 2 very different numbers OR = 044 and RR = 0 Relative risk vs Odds ratio

What Is An Odds Ratio And How Do I Interpret It Critical Appraisal
Odds ratio vs relative risk case control study
Odds ratio vs relative risk case control study-Cohort versus casecontrol studies The study described above is an example of a cohort study, a study in which members of a "The Relative Merits of Risk Ratios and Odds Ratios" Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 1635 (09) • Sainani, Kristin "Understanding Odds Ratios" Physical Medicine and RehabilitationThe proportions of cases & controls exposed to a risk factor of interest are determine and compared by calculating the odds ratio Estimating the OR depends on whether the casecontol study is MATCHED or UNMATCHED



Case Control Study Wikipedia
The risk ratio (or relative risk) is the ratio of the risk of an event in the two groups, whereas the odds ratio is the ratio of the odds of an event (see Box 92a) For both measures a value of 1 indicates that the estimated effects are the same for both interventionsOdds ratio is always larger than Relative Risk, sometimes a lot larger 2 Odds ratios are only useful in true case control studies, which are done because the true incidence of the disease isAn Odds Ratio of unity means that cases are no more likely to be exposed to the risk factor than controls Odds ratio in a matched study In a 11 matching, a case is paired with a control based on a similar characteristic (eg age), and the exposure is assessed in this pair
Here's the key Odds Ratio looks to the past for the cause of a particular effect hence it is used in retrospective studies such as a casecontrol studyAug 26, · Risk ratios, odds ratios, and hazard ratios are three ubiquitous statistical measures in clinical research, yet are often misused or misunderstood in their interpretation of a study's results A 01 paper looking at the use of odds ratios in obstetrics and gynecology research reported 26% of studies (N = 151) misinterpreted odds ratios as risk ratios , while aFeb 24, 13 · ODDS RATIO An odds ratio is the odds of the event in one group , for example, those exposed to a drug, divided by the odds of the event in another group not exposed Odd ratio in epidemiology In case control study since the incidence is not available so relative risk can not be calculated directly Therefore Odd ratio is obtained which is a
Odds Ratio (CaseControl Studies) The odds ratio is a useful measure of association for a variety of study designs For a retrospective design called a casecontrol study, the odds ratio can be used to estimate the relative risk when the probability of positive response is small (Agresti 02)In a casecontrol study, two independent samples are identified based on a binary (yesCase Study Relative Risk and Odds Ratio John Snow's Cholera Investigations Population Information 2 Water Providers Southwark & Vauxhall (S&V) and Lambeth (L) S&V Population # Cholera Deaths 3706 L Poulation # Choleta Deaths 411 Sampling Distribution of RR & OR Goal Obtain Empirical Sampling Distributions of sample RR and OR and observeCaseControl Study and Odds Ratio Learn How to Estimate the Odds Ratio as a Measure of Association for CaseControl Studies?👉🏼 Learn How to Use R to Estim



Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios



Ppt The Odds Ratio Relative Odds Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 6056
The odds ratio from a casecontrol study of the "cumulativeincidence" type can be used as an estimate of the relative risk of a disease attributable to exposure to an agent only when the incidence of the disease is low The odds ratio can be modified to obtain an accurate estimate of the relative risk, regardless of the incidence of the diseaseOdds ratios and logistic regression When a logistic regression is calculated, the regression coefficient (b1) is the estimated increase in the log odds of the outcome per unit increase in the value of the exposure In other words, the exponential function of the regression coefficient (e b1) is the odds ratio associated with a oneunit increase in the exposureApr 14, 17 · Super short post ) Case control study Start with an outcome and go back in time to study the risk factor Simplified Case (Diseased) vs Control (No disease) Cohort study Start with risk factor and see who developed the disease and who did not Mnemonic cOhOrt has two O's One O has an R (cohORt), which means one group has the risk factor Other O does not



Using Odds Ratio In Case Control Studies Youtube



Cohort Case Control Studies Http Www Slideshare Net Terryshaneyfelt7 What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative R Cohort Study Academic Research Research Methods
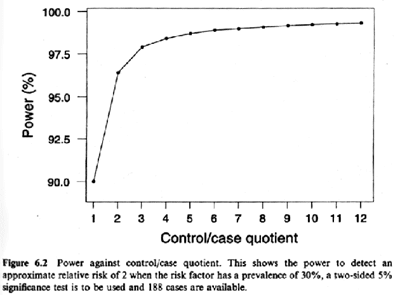
Suppose your study design is an unmatched casecontrol study with equal numbers of cases and controls If 30% of the population is exposed to a risk factor, what is the number of study subjects (assuming an equal number of cases and controls in an unmatched study design) necessary to detect a hypothesized odds ratio of ?Mar 28, 1998 · Odds ratios are a common measure of the size of an effect and may be reported in casecontrol studies, cohort studies, or clinical trials Increasingly, they are also used to report the findings from systematic reviews and metaanalyses Odds ratios are hard to comprehend directly and are usually interpreted as being equivalent to the relative riskFor casecontrol trials we use odds ratio to compare the "incidence" of past exposures or treatments Cohort Studies (and clinical trials) –> Relative Risk CaseControl studies –> Odds Ratio I remember this by thinking about a group of pirates (group = cohort) all saying "aRRrrr!"



Estimated Relative Risk Odds Ratio Or Hazard Ratio With 95 Ci For 4 Download Scientific Diagram



Relative And Attributable Risks Absolute Risk Involves People
Mar 14, 16 · In a casecontrol study, it is said that we can approximate relative risk (RR) by odds ratio (OR) when the disease is rare O R = p 1 1 − p 1 p 2 1 − p 2 = p 1 p 2 1 − p 2 1 − p 1 = R R 1 − p 2 1 − p 1 But there is one thing that I do not understandOct 27, 11 · In contrast in casecontrol studies, incidence data is usually not available Therefore, the ratio of the odds of exposure among cases to the odds of exposure among noncases is calculated In theory, all casecontrol studies can be viewed as nested casecontrol studies, in which both cases and controls are drawn from a well defined sourceIf the disease is rare, the odds ratio is a good estimate of the relative risk common disease showing relative risk and odds ratio being different if youve got an RR over 1, the odds ratio will generally be a little bit higher



Solved Select All Of The True Statements Regarding The Od Chegg Com



Relative Risk Or Odds Ratio For Cardiovascular Disease Incidence Download Scientific Diagram
When you estimate the risk in a casecontrol study, you estimate the likelihood of having the exposure in those who have the disease, relative to those who do not Now, I will work through an example of how to calculate and interpret the odds ratio in a case control study, examining the association between smoking and lung cancerJul 11, 16 · If O1 is the odds of event in the Treatment group and O2 is the odds of event in the control group then the odds ratio is O1/O2 Just like the risk ratio, it's a way of measuring the effect of the tutoring program on the odds of an eventMar 19, 18 · In addition, one can also calculate an odds ratio in a cohort study, as we did in the two examples immediately above In contrast, in a casecontrol study one can only calculate the odds ratio, ie an estimate of relative effect size, because one cannot calculate incidence



How To Interpret And Use A Relative Risk And An Odds Ratio Youtube


Solved A Prospoctive Cohort Study B Case Control Study Chegg Com
I understand that odds ratio is the ratio is the odds of two groups (ie positive outcomes/negative outcomes), where as relative risk is the ratio of risk of two groups (ie positive outcomes/all outcomes)The odds ratio is a useful measure of association for a variety of study designs For a retrospective design called a casecontrol study, the odds ratio can be used to estimate the relative risk when the probability of positive response is small (Agresti, 02)In a casecontrol study, two independent samples are identified based on a binary (yesno) response variable, and theIn epidemiological terms, the odds ratio is used as a point estimate of the relative risk in retrospective studies Odds ratio is the key statistic for most casecontrol studies In prospective studies, Attributable riskor risk difference is used to quantify risk in the exposed group that is attributable to the exposure



What Is An Odds Ratio And How Do I Interpret It Critical Appraisal



Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us CreatorsTherefore, odds ratios from most casecontrol studies can be interpreted as risk ratios However, if a study outcome is common, the odds ratio will be furtherCalculating Odds Ratio in a CaseControl Study Case Control History of Exposure a b No History of Exposure c d OR = odds that a case was exposed OR = a c b d = a c x d b = ad bc 32 Odds Ratio versus Relative Risk Odds ratio can be calculated in a cohort study and in a casecontrol study



Related Image Cross Sectional Study Hazard Ratio Odds



Observational Studies The Ebm Project
Could someone explain why odds ratios are used in case control studies where as relative risk is used in RCT and cohort studies?Oct 01, 07 · In a case–control study, the odds of exposure in cases and controls are calculated as the number of exposed individuals divided by the number of unexposed individuals in each group If we know the odds of exposure in cases and controls, we can calculate the OR, that is the ratio between the odds of exposure in diseased and in nondiseasedRelative risk, odds, odds ratio, and others The concept and method of calculation are explained for each of these in simple terms and with the (RCTs), cohort studies, and casecontrol studies Nevertheless, similar principles operate when these concepts are applied in epidemiologic



A Practical Overview Of Case Control Studies In Clinical Practice Chest


Case Control Study Odds Ratio Relative Risk Best Custom Academic Essay Writing Help Writing Services Uk Online Homeworknowcomlink Web Fc2 Com
In casecontrol studies when the risk of a disease cannot be known;Apr 06, 10 · The Odds Ratio can be addressed by asking te following question How many times more likely is a diseased group to have been exposed to a risk factor as compared to a nondiseased group?Apr , · Relative risks and odds ratios are widely reported in the medical literature, but can be very difficult to understand We sought to further clarify these important indices Methods We illustrated both relative risks and odds ratios using bar charts, then looked at the types of study for which each statistic is suited We demonstrated


Case Control Study Odds Ratio Relative Risk Best Custom Academic Essay Writing Help Writing Services Uk Online Homeworknowcomlink Web Fc2 Com



Flowchart Of Study Selection Process Hr Hazard Ratios Or Odds Download Scientific Diagram
Odds Ratio (CaseControl Studies) The odds ratio is a useful measure of association for a variety of study designs For a retrospective design called a casecontrol study , the odds ratio can be used to estimate the relative risk when the probability of positive response is small (Agresti 1990)In clinical studies, as well as in some other settings, the parameter of greatest interest is often the relative risk rather than the odds ratio The relative risk is best estimated using a population sample, but if the rare disease assumption holds, the odds ratio is a good approximation to the relative risk — the odds is p / (1 − p), so when p moves towards zero, 1 − p moves towards 1May 04, 09 · When a study outcome is rare in all strata used for an analysis, the odds ratio estimate of causal effects will approximate the risk ratio;


Case Control Study Odds Ratio Relative Risk Best Custom Academic Essay Writing Help Writing Services Uk Online Homeworknowcomlink Web Fc2 Com



Estimating Risk
May 18, 12 · The odds ratio is the measure of choice in a casecontrol study (see Lesson 1) A casecontrol study is based on enrolling a group of persons with disease ("casepatients") and a comparable group without disease ("controls") The number of persons in the control group is usually decided by the investigatorAlthough in classical casecontrol studies, it remains true that the odds ratio can only approximate the relative risk in the case of rare diseases, there is a number of other types of studies (casecohort, nested casecontrol, cohort studies) in which it was later shown that the odds ratio of exposure can be used to estimate the relative riskThe odds ratio is the "measure of association" for a casecontrol study It quantifies the relationship between an exposure (such as eating a food or attending an event) and a disease in a casecontrol study



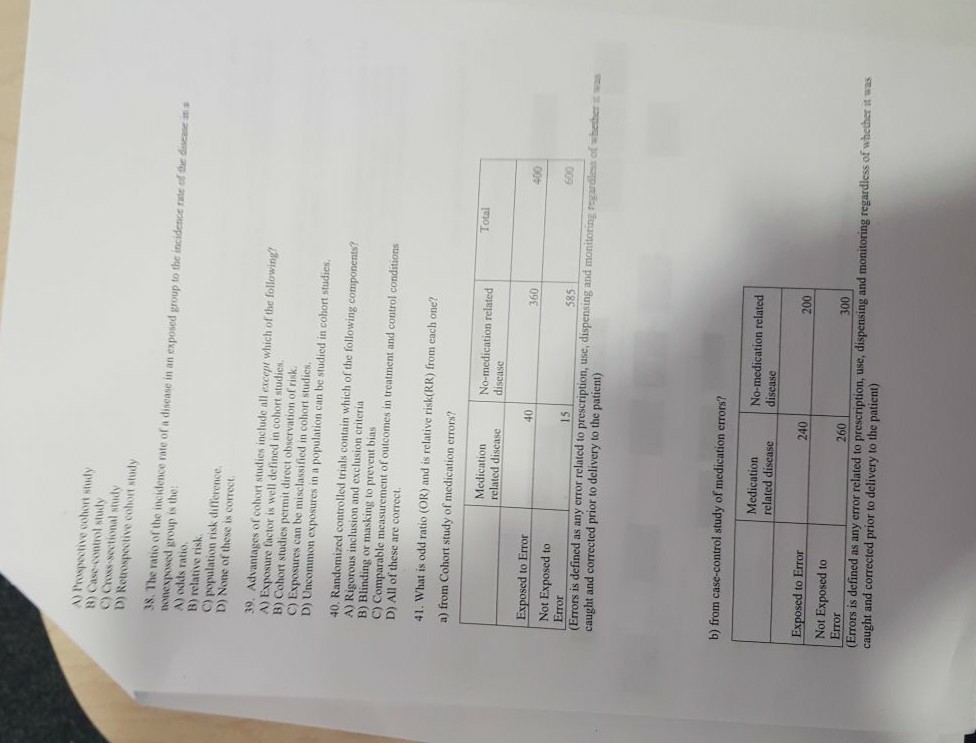
Odds Ratio Relative Risk Risk Difference With R R Tutorial 4 11 Marinstatslectures Youtube


Case Control Study Part 2
Casecontrol studies The odds ratio is the measure of association for a casecontrol study It tells us how much higher the odds of exposure is among cases of a disease compared with controls The relative risk is the ratio of the attack rates ofNov 18, 1998 · When the risk ratio cannot be obtained directly (such as in a casecontrol study), the odds ratio is calculated and often interpreted as if it were the risk ratio Subsequently, the term relative risk commonly refers to either the risk ratio or the odds ratioOdds ratios (OR) are commonly reported in the medical literature as the measure of association between exposure and outcome However, it is relative risk that people more intuitively understand as a measure of association Relative risk can be directly determined in a cohort study by calculating a risk ratio (RR)



Relative And Atribute Risk



Case Control Study Wikipedia
In the example above the casecontrol study of only 79 subjects produced an odds ratio (656) that was a very close approximation to the risk ratio (652) that was obtained from the data in the entire populationThis chapter uses odds ratios from casecontrol studies for the same purpose We will discuss the sampling theory behind casecontrol studies in lecture For details, estimate of the relative incidence (relative risk) of the outcome associated with exposure (assuming data are errorfree)How do you estimate the relative risk then in a case control study?



Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk Difference And Number Needed To Treat Sciencedirect



Cecile Janssens A Reminder That Odds Ratios Massively Overestimate Relative Risks When Outcome Is Common In The Population Or By Study Design E G Case Control Studies Io Is Proportion Of Cases



Beabletocalculate Direct Age Adjustment Proport Chegg Com



How To Calculate An Odds Ratio Youtube



The Difference Between A Retrospective Cohort Study And A Prospective Cohort Study Case Control Study Cohort Study Study



Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1



Using Odds Ratio In Case Control Studies Youtube Case Control Study Study Parenting Advice


Estimating Risk



Relative Risks Rrs In Prospective Studies Or Odds Ratios Ors In Download Scientific Diagram



1 The Odds Ratio Relative Odds In A Case Control Study We Do Not Know The Incidence In The Exposed Population Or The Incidence In The Nonexposed Population Ppt Download



Analytical Studies Note Cohort Study Gives Incidence Relative Risk A R P A R Natural History Of Disease Cohort Study Case Control Study Study



Case Control Study And Odds Ratio Statistics Tutorial 31 Marinstatslectures Youtube



Figure 2 From Secondhand Smoke Exposure And Risk Of Lung Cancer In Japan A Systematic Review And Meta Analysis Of Epidemiologic Studies Semantic Scholar


Measures Of Association Ppt Download



Case Control Cohort Studies Ppt Video Online Download



Pair Matched Case Control Table



Evidence Of Safety Pooled Relative Risk Rr Or Odds Ratio Or And Download Table



A Practical Overview Of Case Control Studies In Clinical Practice Chest



Believability Of Relative Risks And Odds Ratios In Abstracts Cross Sectional Study The Bmj


Case Control Studies



The Difference Between Relative Risk And Odds Ratios The Analysis Factor



Relative And Attributable Risks Absolute Risk Involves People



Measures Of Association Ppt Download



Calculation Of Relative Risks Rr And Odd Ratios Or Download Table



Calculation Of The Odds Ratio In A Case Control Study The Upper Panel Download Scientific Diagram


Case Control Study Vs Cohort Study Pp Made Easy In Population Perspective Made Easy On Vimeo



Observational Studies The Ebm Project


Introduction To Genetic Epidemiology Lesson 5 Analyzing The Data



Case Control Cohort Study


9 5 Example 9 3 Odds Ratios From A Case Control Study



Forest Plot Of Relative Risks And Odds Ratios Of Lung Cancer Associated Download Scientific Diagram



Pair Matched Case Control Table



Case Control Study 8 21 152 Case Control Study Exposure Disease Exposure Disease Ppt Download



Measures Of Association Ppt Download


Case Control Studies



Forest Plot Of Relative Risks And Odds Ratios Of Lung Cancer Associated Download Scientific Diagram



Odds Ratio Litfl Ccc Research
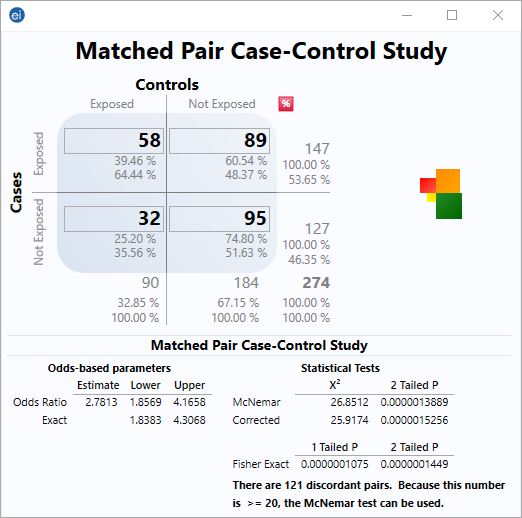


Matched Pair Case Control Statcalc User Guide Support Epi Info Cdc



Lecture 08 Strategies For Data Analysis Cohort And Case Control Studies Ppt Relative Risk Cohort Study


Case Control Studies Howmed



Relative Risk Wikipedia



Please Fill Out Table 8 Below Using The Results Fr Chegg Com



Pdf When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk



Using Odds Ratio In Case Control Studies Youtube



Cohort And Case Control Research Ppt Video Online Download


Relative Risk Wikipedia


9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 Review Odds Ratios Are Calculated From Case Control Studies Which Are Described On Slide 14 Odds Ratios Are Only Estimates Of Relative Risks Since True Incidence Rates Cannot Be
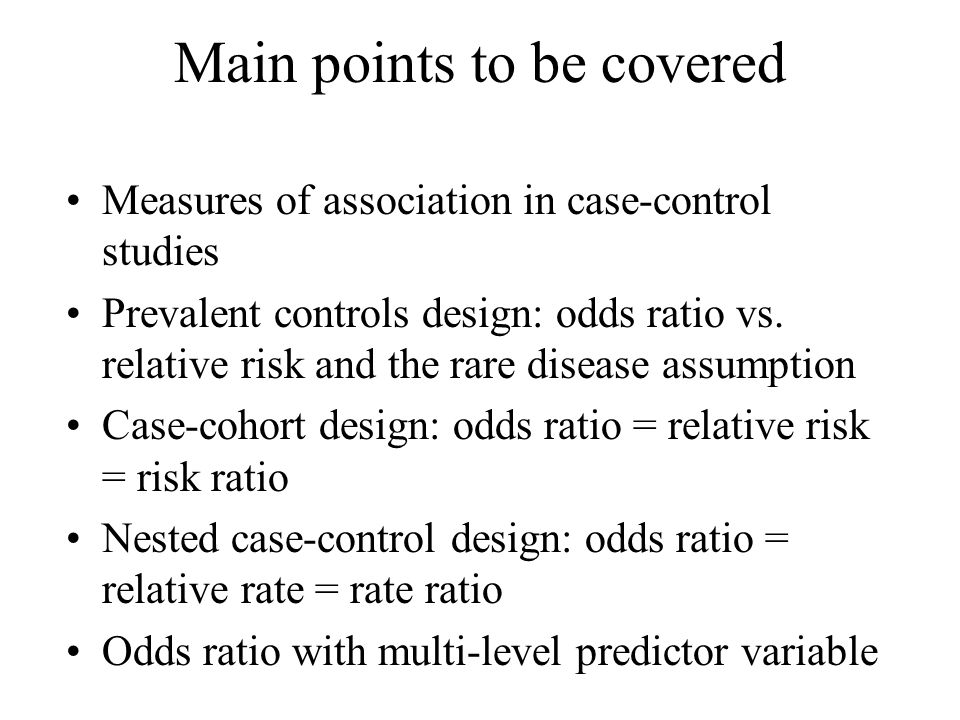


Main Points To Be Covered Measures Of Association In Case Control Studies Prevalent Controls Design Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk And The Rare Disease Ppt Download



Calculation Of Odds Ratios Or And Relative Risk Rr Derived From Download Scientific Diagram



Biostatistics Flashcards Quizlet


Introduction To Genetic Epidemiology Lesson 5 Analyzing The Data



Relative Risks And Odds Ratios What S The Difference Mdedge Family Medicine



Cph Exam Review Epidemiology Ppt Download



Odds Ratio Relative Risk Calculation Definition Probability Odds Youtube



What Is The Difference Between The Risk Ratio Rr And The Odds Ratio Or Quora
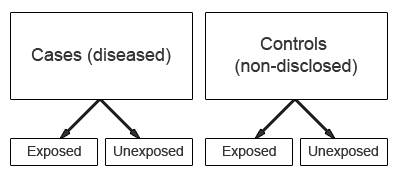


Introduction To Study Designs Case Control Studies Health Knowledge
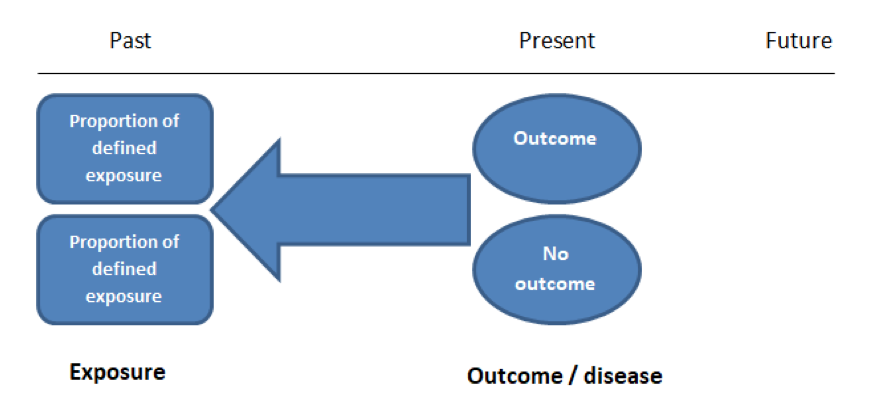


Case Control And Cohort Studies A Brief Overview Students 4 Best Evidence



Relative Risk Odds Ratios Youtube



Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk Difference And Number Needed To Treat Sciencedirect



Epidemiology Calculating Relative Risk Youtube


Icare An R Package To Build Validate And Apply Absolute Risk Models


Analytical Studies



What Is An Odds Ratio And How Do I Interpret It Critical Appraisal



Odds Ratio Article


Case Control Studies Howmed



Math3010 Week 6


Case Control Study Vs Cohort Study Pp Made Easy In Population Perspective Made Easy On Vimeo



Epidemiology Odds Ratio Or Bean Around The World


Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1



Ppt The Odds Ratio Relative Odds Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 6056



Odds Ratios For Case Control Data In Stata Youtube



Calculating Matched Pairs Odds Ratio Youtube



Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1



Statistics Part 13 Measuring Association Between Categorical Data Relative Risk Odds Ratio Attributable Risk Logistic Regression Data Lab Bangladesh



Society For Birth Defects Research And Prevention
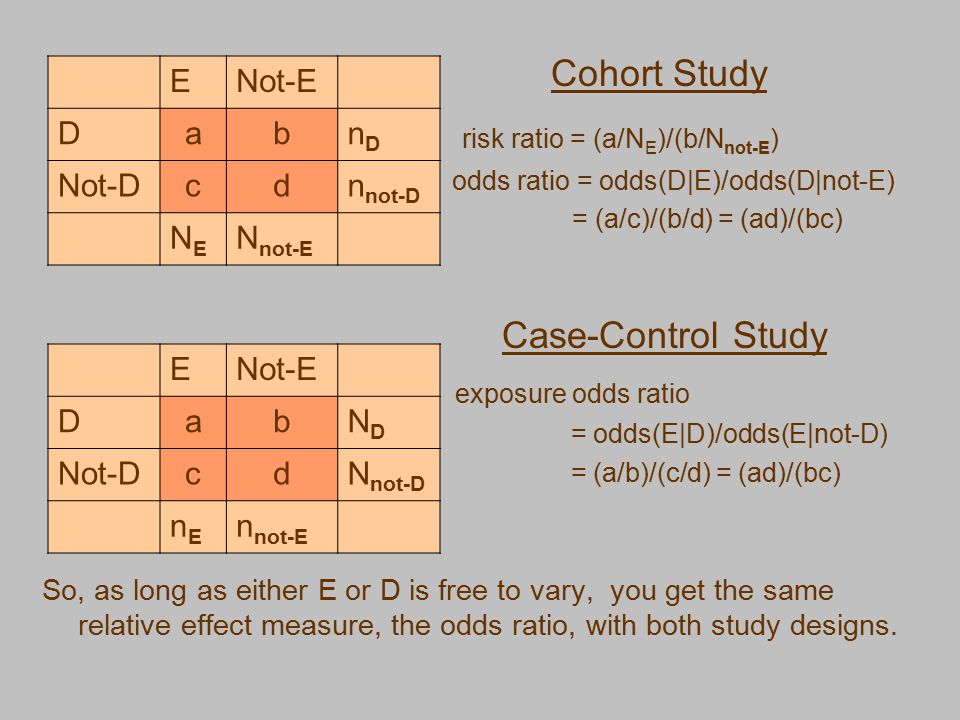


Case Control Studies Statistical Analysis Ppt Video Online Download



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿